Researchers identify 21 modifiable risk factors for reducing the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
The APOE gene is one of the most-significant genetic risk factors associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. But many people, even those with a family history of Alzheimer’s, have often hesitated before taking a DNA test to assess their risk, until now.
A recent study finds that as many as 19 risk factors associated with Alzheimer’s disease may be modifiable. Keeping your heart healthy, engaging your brain often, maintaining a healthy body weight and reducing stress levels are among the top 10 preventative factors associated with developing Alzheimer’s.
Nine additional factors such as regular exercise, good sleep, abstaining from smoking and including vitamin C in your diet may also reduce your risk, according to this study. Healthcare providers can now use these evidence-based guidelines to personalize preventative options, particularly for those who carry the APOE risk allele.
Risk of Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s is the most common progressive brain disorder to affect the elderly. Approximately 1 in 10 people over the age of 65 have late-onset Alzheimer’s. It is estimated 131 million people worldwide will be affected by 2050.
Age, family history and genetic are the three main factors linked to Alzheimer’s. One genetic variant in the APOE gene is one of the biggest genetic risk factors. Individuals who inherit the APOE e4 variants are at 3 to 15 times higher risk of developing the disease.
Top preventative actions to take
While previous studies have identified factors linked to prevention, interpreting and consolidating, these findings have been difficult. Hence, the researchers in this study combined data from 395 previously published studies to formulate evidence-based clinical guidelines for Alzheimer’s prevention.
The following are the top 10 modifiable risk factors identified in this meta-analysis.
- Extending early education years
- Keeping the brain active as long as possible
- Avoiding high blood pressure, particularly in the middle age
- Addressing low blood pressure when you stand from sitting up or lying down (known as orthostatic hypotension)
- Controlling your blood sugar levels
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Minimizing trauma to the head
- Maintaining healthy levels of homocysteine, a substance linked to increase blood clots and blood vessel damage
- Treating depression
- Avoiding stress
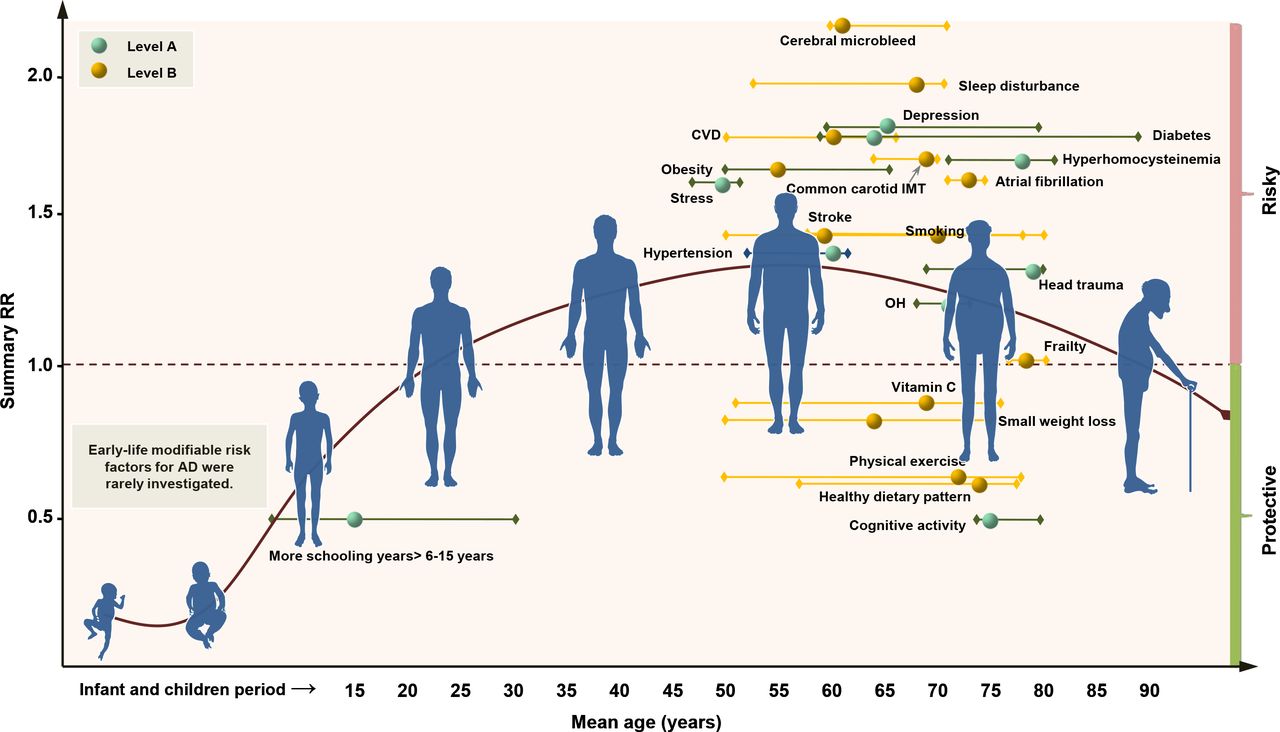
The study also suggested nine other preventative actions including regular exercise, avoiding smoke exposure, attaining good sleep, good heart health and increasing vitamin C intake. The study also identified two existing interventions that should be avoided. These included estrogen replacement therapy and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Personalized prevention for Alzheimer’s disease
There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. However, we now have an evidence-based list of preventative measures that reduce one’s risk. These modifiable actions are highly relevant individuals at higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, such as those with a family history or carry genetic variants of the APOE gene.
The study recommends identifying high-risk individuals early on and tailoring these preventative measures to best suit each patient. If you have been hesitant about taking a DNA test to assess your risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, here is your chance.
Take an actionable DNA test to uncover your risk of Alzheimer’s disease, so you can work with your healthcare provider to modify your genetic risk.
Reference:
Yu J, Xu W, Tan C, et al. (2020) Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-321913.